
In international logistics, the choice between Full Container Load (FCL) and Less than Container Load (LCL) shipping is a crucial decision that can impact cost, transit time, and handling requirements. Understanding the differences and applications of FCL and LCL is essential for businesses looking to optimize their shipping strategies. In this blog, we explore the nuances of FCL and LCL in international logistics and how to choose the best option for your shipping needs.
FCL refers to shipping a container filled with one shipper's goods. It is ideal for larger shipments where the volume of goods is enough to fill an entire container.
Cost Efficiency: For large shipments, FCL can be more cost-effective than LCL, as you pay for the entire container at a fixed rate.
Faster Transit Time: FCL shipments are typically faster than LCL since they require less handling and fewer stops.
Reduced Handling: With FCL, the container is sealed at the origin and opened at the destination, minimizing the risk of damage.
LCL involves shipping goods that do not fill an entire container and are consolidated with other shippers' goods. It’s a popular choice for smaller shipments.
Flexibility: LCL offers flexibility for smaller shipments, allowing shippers to pay only for the space they use.
Cost-Effective: For smaller volumes, LCL can be more economical than paying for an entire container.
Regular Departures: LCL services often have more regular departures, providing more options for shippers.
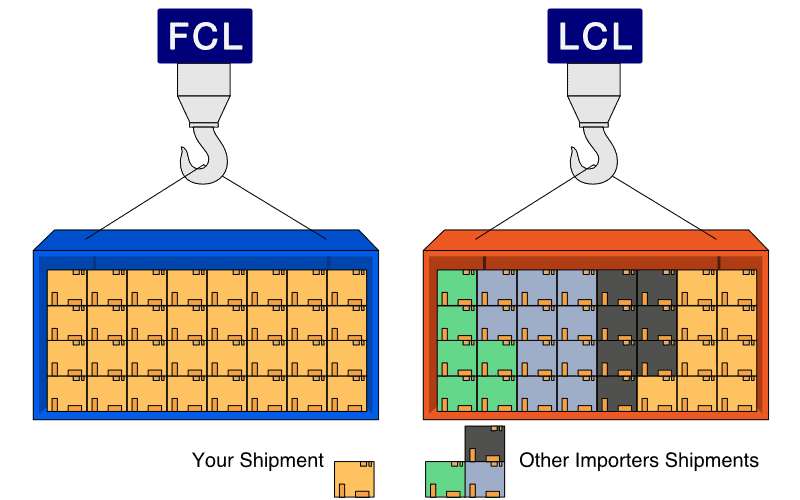
Volume and Size of Shipment
FCL is typically chosen for shipments large enough to fill a container.
LCL is suitable for smaller shipments that cannot justify the cost of an entire container.
Cost Considerations
Analyze the cost differences between FCL and LCL, considering the size and nature of your cargo.
Transit Time
FCL generally offers faster transit times and fixed departure dates.
LCL might involve longer transit times due to additional handling and consolidation processes.
Risk of Damage
FCL reduces the risk of damage through less handling.
LCL might have a higher risk due to multiple handling and consolidation.
Warehousing Needs
FCL shipments might require more storage space at the destination.
LCL allows for smaller storage space and could be beneficial for businesses with limited warehousing capacity.
The decision between FCL and LCL in international logistics depends on the specific needs of your shipment, including size, cost, transit time, and handling requirements. By understanding the advantages of each and assessing your shipping needs, you can make an informed decision that balances cost, efficiency, and safety. Whether choosing FCL or LCL, the key is to align your choice with your overall logistics strategy and business objectives.

Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.
Wing Shipping offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air, sea, and rail freight. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Copyright 2024 Wing-Shipping. All Rights Reserved.